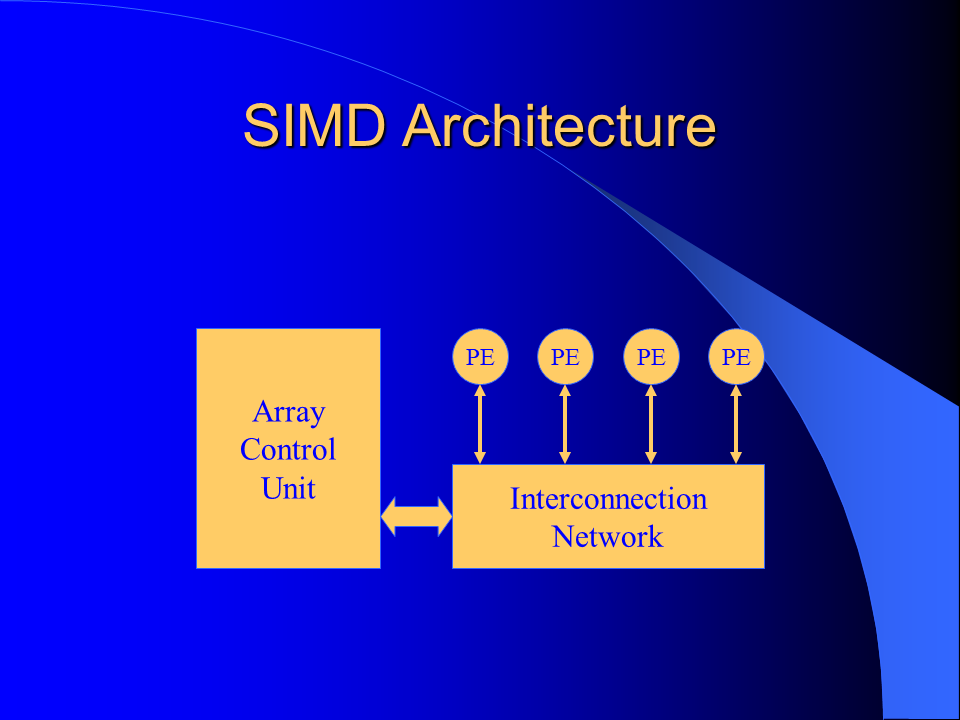
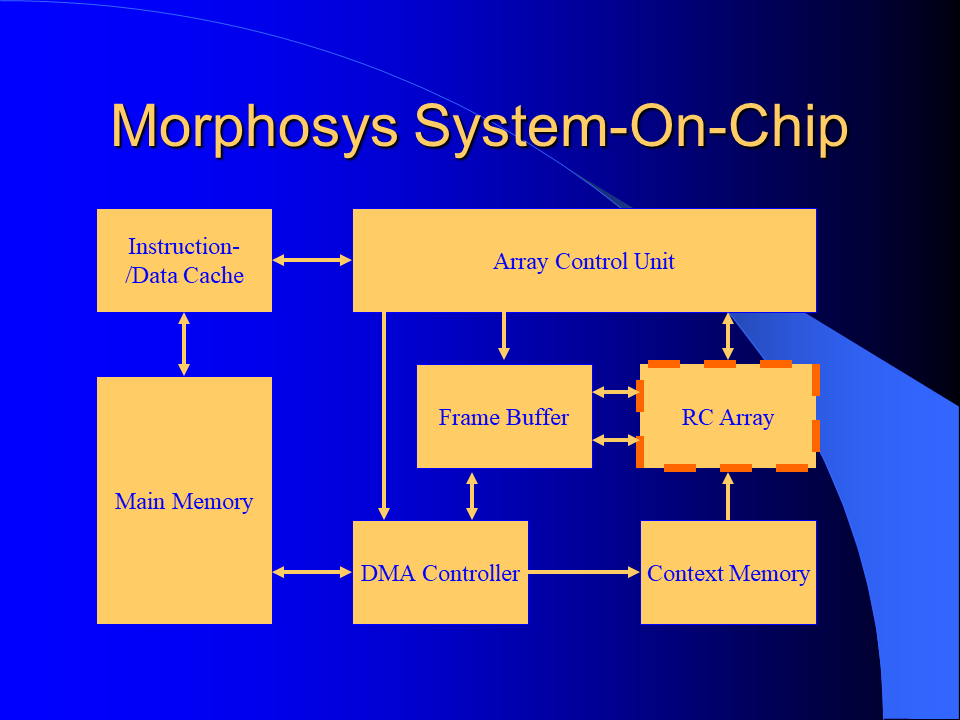
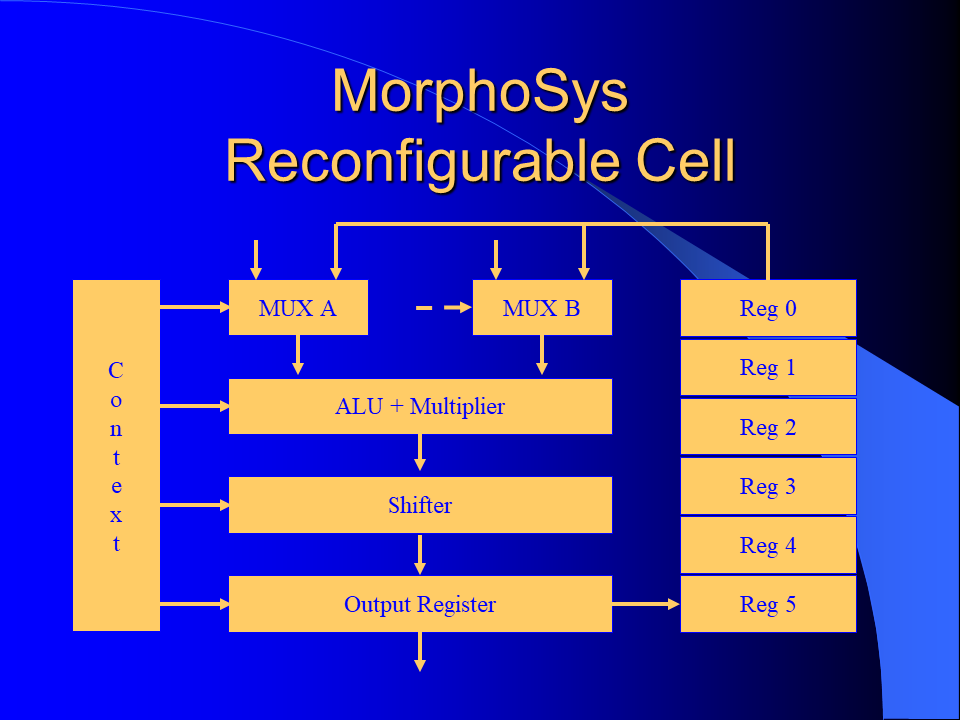
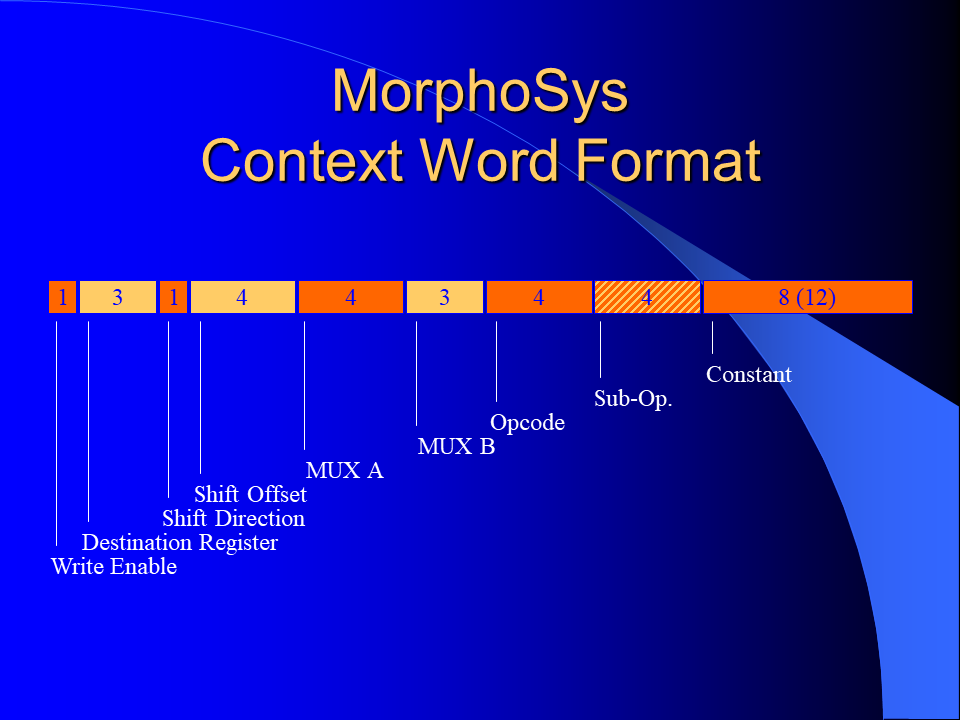
MorphoSys is a reconfigurable computer architecture that is composed of a software programmable processing unit called TinyRISC and a reconfigurable hardware unit called Reconfigurable Cell Array (RC Array). The Reconfigurable Cell Array has 64 reconfigurable cells arranged in an 8 by 8 array. Each cell has an ALU/MAC unit and a register file. RC Array functionality and the interconnection network are configured through context words. Context words are stored in a context memory in two blocks (one for the rows and the other one for the columns). Each block has eight sets of sixteen context words.
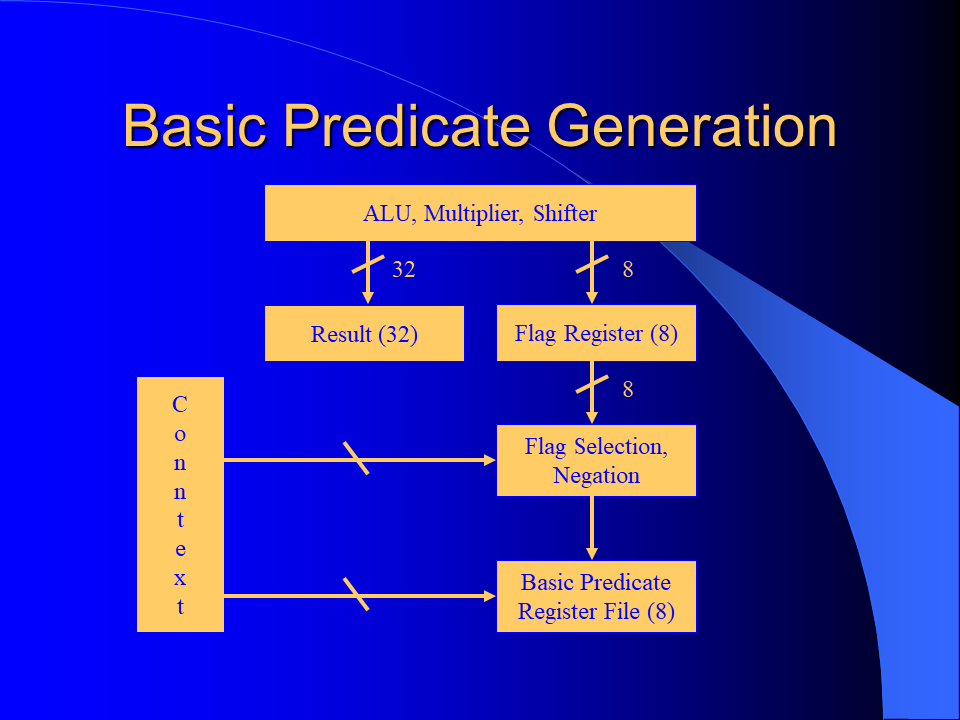
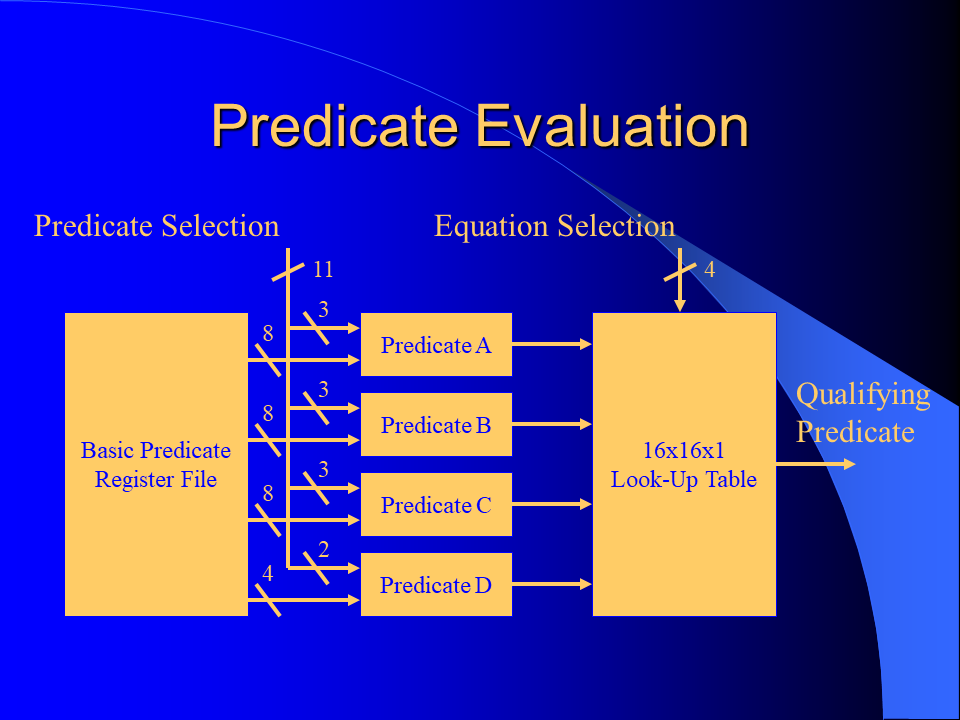
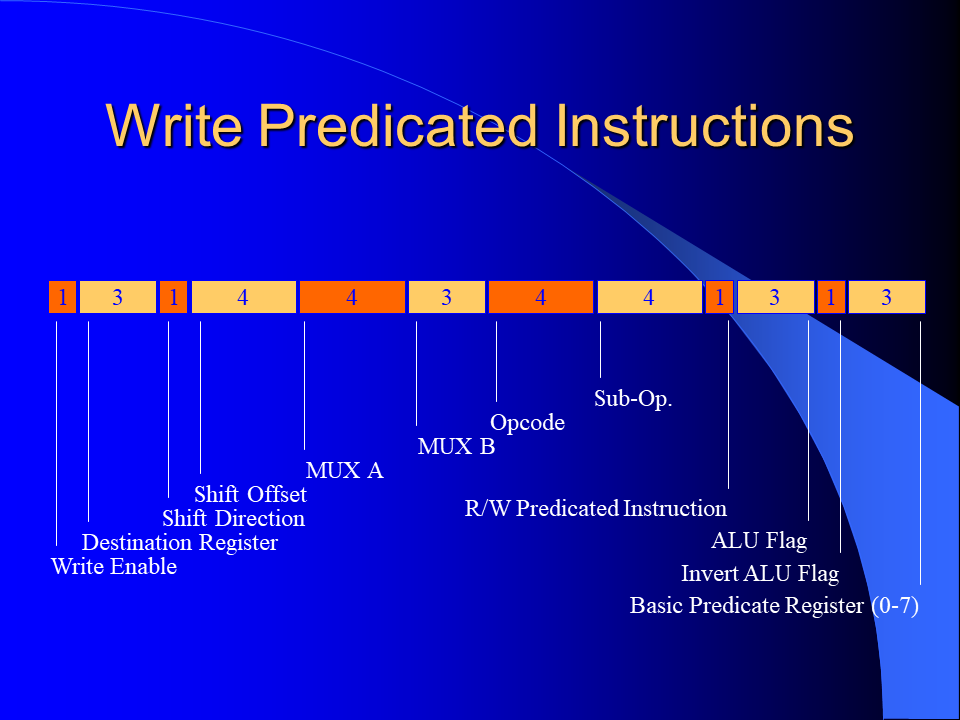
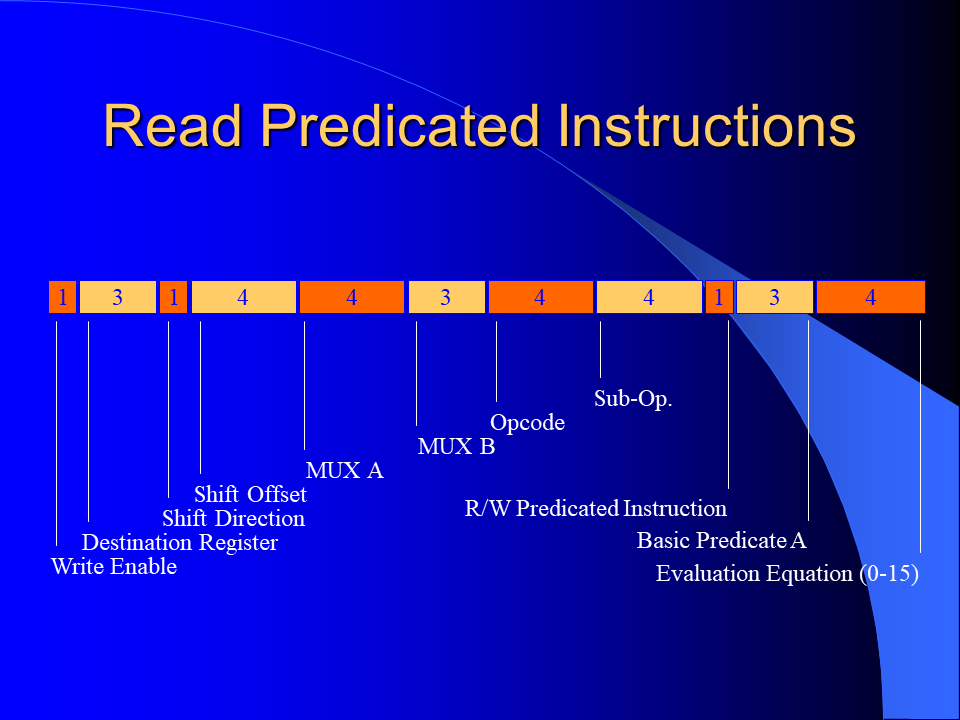
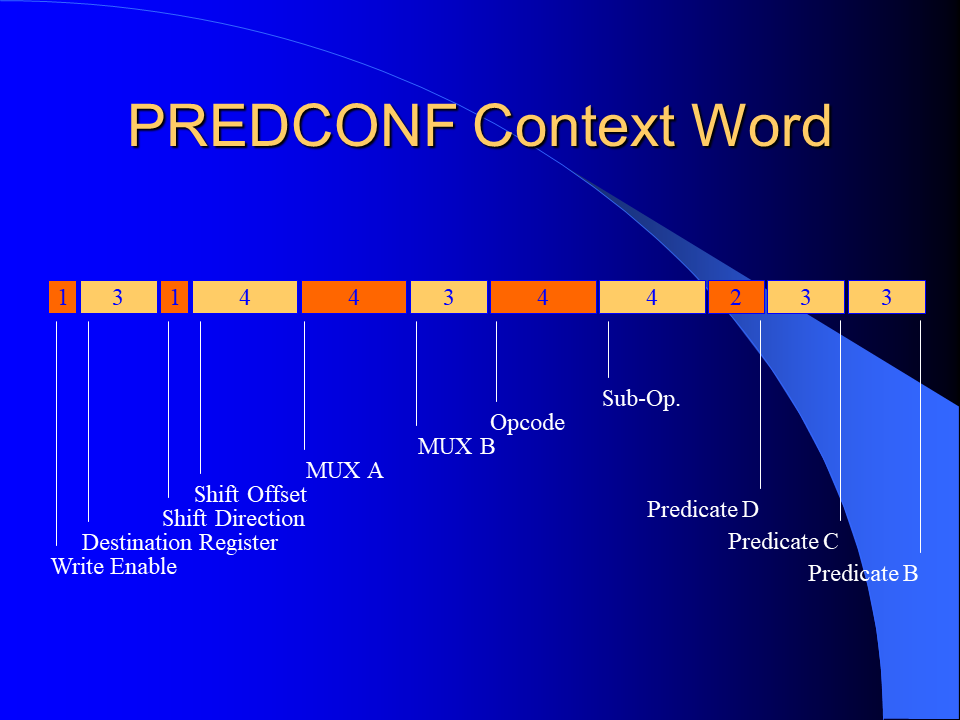
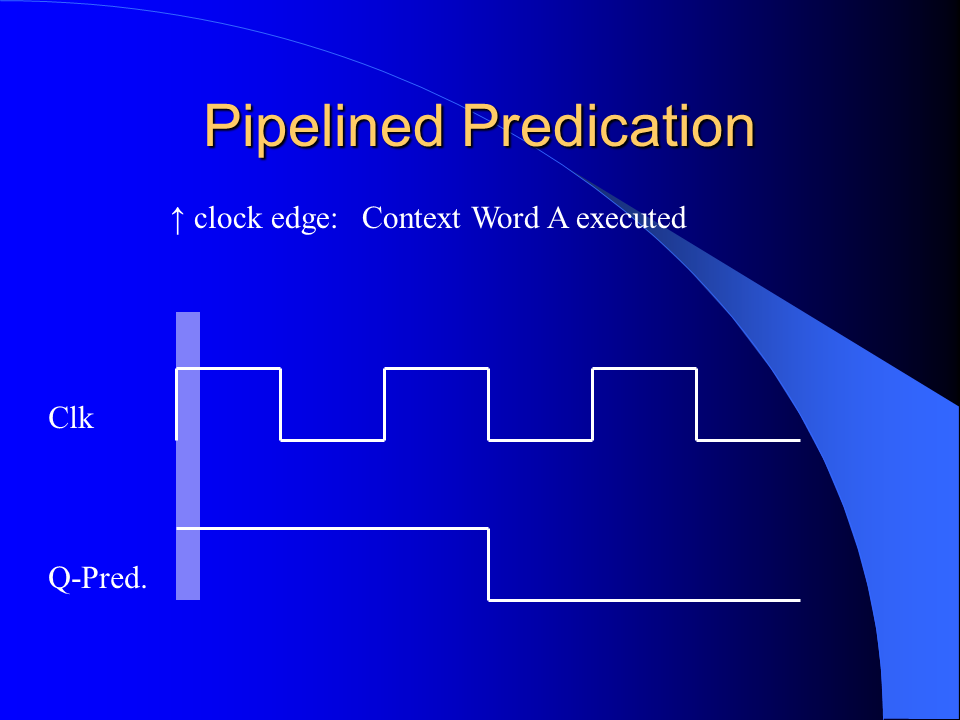
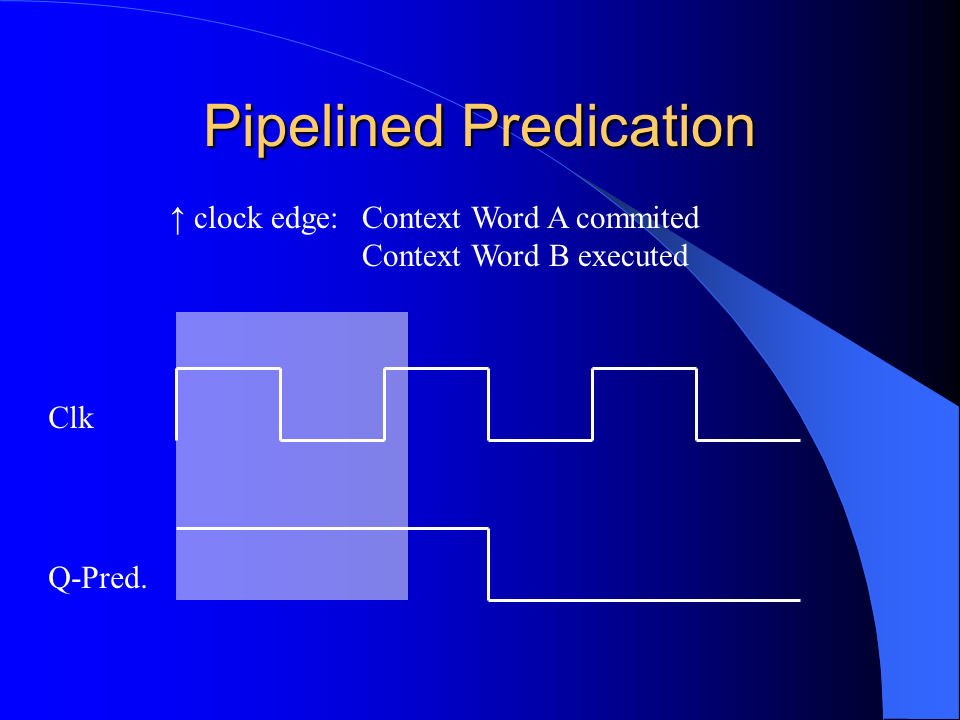
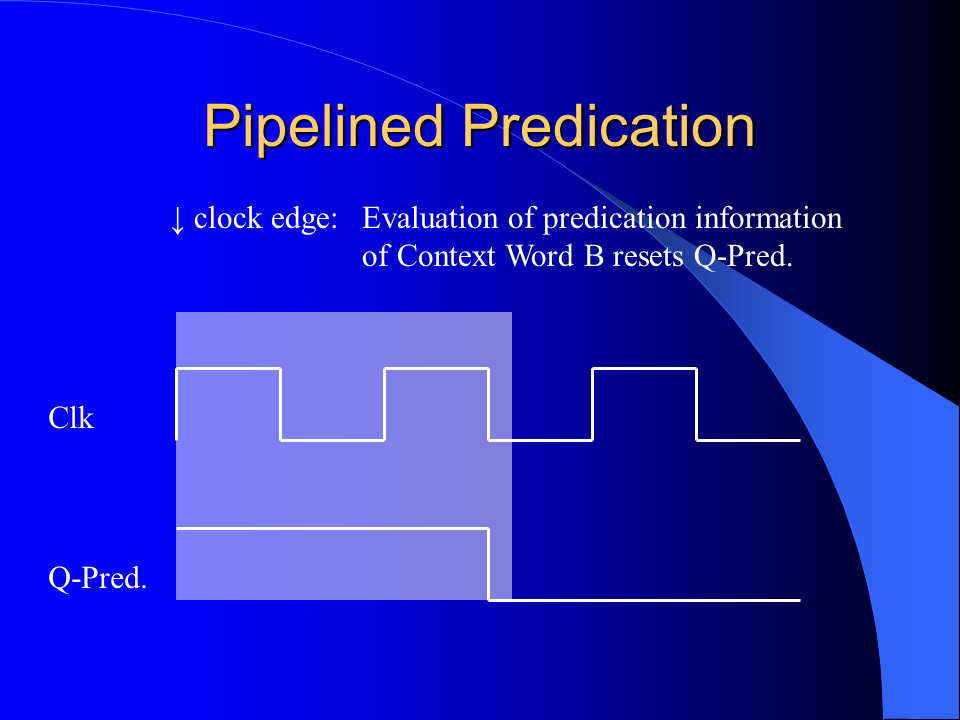
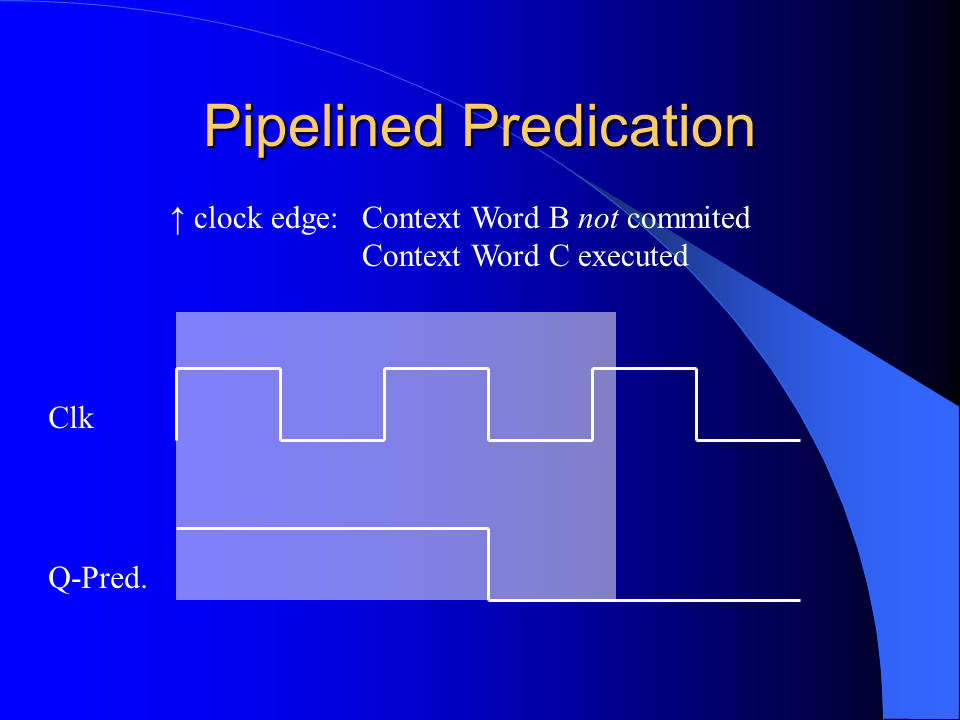
I developed a novel branch predication scheme for the MorphoSys Reconfigurable Cell Array by improving and combining the unrestricted predication model and the guarded execution model. It could be shown that significant execution autonomy was added to the SIMD processing elements and that the code size was reduced considerably. The implemented predication scheme enables more efficient if-conversion compilations than previous predication schemes of general purpose processors.
This work was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) (DoD) under contract F-33615-97-C-1126 and by the National Science Foundation under grant CCR-0083080.
Publications
| 2003 | 1st Workshop on Embedded Systems for Real-Time Multimedia (ESTIMedia) | A Component Oriented Simulator for HW/SW Co-Designs | BibTeX |
| 2002 | 8th Euro-Par | A Novel Predication Scheme for a SIMD System-On-Chip | BibTeX |
| 2002 | 15th Brazilian Symposium on Integrated Circuit Design (SBCCI) | A Novel Method for Improving the Operation Autonomy of SIMD Processing Elements | BibTeX |
| 2002 | 5th Euromicro Symposium on Digital System Design (DSD) | Improving the Operation Autonomy of SIMD Processing Elements by Using Guarded Instructions and Pseudo Branches | BibTeX |
| 2002 | Diplomarbeit, Universität Karlsruhe (TH) | A Novel Predication Scheme for a SIMD System-On-Chip developed with a Component Oriented Simulator | BibTeX |